Inflation: Understanding the Phenomenon
Inflation is a monetary term that alludes to the supported expansion in the general value level of labour and products in an economy over a particular time frame. By and large, the buying force of a unit of cash is diminishing.
Inflation can be estimated by following the rate change in a bin of labour and products, known as the Customer Value Record (CPI), which addresses what a typical shopper buys. There are different reasons for Inflation, with request pull inflation and cost-push expansion being the two essential classifications. Request pull expansion happens when there is an expansion in customer interest for labour and products that dominates the economy's ability to create them. This frequently occurs during times of financial development, and it can prompt a circumstance where an excess of cash pursues too couple of merchandise, driving costs up. Then again, cost-push inflation emerges from an expansion in the creation expenses of labour and products. This can be because of variables like rising wages, expanded unrefined substance costs, or other stockpile side imperatives. At the point when the expense of creation rises, makers will generally pass those expenses onto customers as more exorbitant costs, bringing about expansion.
Inflation Rate: Quantifying the Impact
The Inflation rate, an essential monetary marker, evaluates the rate change in the general value level of labour and products over a particular period, normally estimated on a yearly premise. It gives a depiction of how quick costs are ascending in an economy. To compute the expansion rate, one purposes a base year's CPI as a kind of perspective point. The recipe for this computation is: Inflation Rate=(CPI in Current Year−CPI in Base Year CPI in Base Year)×100 Inflation Rate= ( CPI in Current Year−CPI in Base Year Isolated by CPI in Base Year ) x 100 Understanding the Inflation rate is urgent for both policymakers and people. For policymakers, it illuminates choices about money related approach, financing costs, and other monetary mediation. A moderate degree of expansion is by and large thought to be ordinary in a developing economy, yet unreasonable expansion can disintegrate buying power and upset monetary steadiness. For people, the expansion rate straightforwardly influences their typical cost for many everyday items. At the point when costs rise quicker than wages, it can prompt a decrease in genuine buying power. For instance, on the off chance that an individual's pay increments by 3% in a year, however the expansion rate is 4%, they are really losing buying power. In addition, the Inflation rate likewise influences speculation choices. Financial backers plan to procure a profit from their speculations that surpasses the pace of expansion. Assuming that the expansion rate is high, it turns out to be more difficult to accomplish genuine returns, which can impact venture methodologies. In synopsis, Inflation is a basic monetary idea that influences both the macroeconomic strength of a nation and the monetary prosperity of people. The expansion rate, as a quantifiable proportion of this peculiarity, gives important data to monetary strategy choices and individual monetary preparation. Understanding these ideas engages people to settle on informed monetary choices and adds to a more steady and prosperous economy.
Major Causes Of Boosted Inflation :
Request Pull Expansion:
- Expanded Purchaser Spending: When buyers have more discretionary cash-flow and choose to spend it, the interest for labour and products rises. This can prompt greater costs as makers battle to stay aware of the expanded interest. Government Spending: Government consumption on ventures, government assistance, or protection can infuse extra cash into the economy. Assuming that this spending outperforms the economy's ability to deliver, it can bring about expanded request and hence, expansion.
- Cost-Push Expansion:
- Rising Creation Expenses: Any expansion in the expenses of data sources like work, unrefined components, or energy can raise creation costs for organisations. To keep up with their net revenues, they might increment costs, prompting expansion. Inventory network Interruptions: Occasions like catastrophic events, exchange limitations, or international contentions can disturb the progression of labor and products. This can prompt deficiencies, which, thusly, can raise costs because of expanded rivalry for restricted assets. Wage Push: On the off chance that wages increment without comparing upgrades in efficiency, organizations might raise costs to take care of the greater work costs, prompting expansion.
- Underlying Expansion:
- Assumptions for Future Expansion: When people or organizations guess that costs will ascend from here on out, they might go to proactive lengths. This can incorporate requesting higher wages, which can set off a pattern of increasing expenses and costs. Financial Arrangement: Extreme Cash Supply: On the off chance that a national bank expands the cash supply too quickly, it can prompt an oversupply of cash comparative with accessible labor and products. This can cause expansion as an excess of cash pursues too couple of merchandise. Low Loan costs: When national banks keep up with low loan fees, getting becomes less expensive. This can invigorate spending and speculation, prompting expanded request and possibly, inflationary tensions.
- Outer Shocks:
- International Occasions: Wars, political insecurity, or exchange clashes can upset creation and exchange. This prompts marked down supply and inflated costs, which can bring about more exorbitant costs. Catastrophic events: Occasions like tremors, tropical storms, or dry seasons can harm foundation, disturb creation, and weaken supply chains. This can prompt scaled down accessibility of labor and products, making costs rise.
- Conversion scale Developments:
- Deterioration of Cash: When a country's money loses esteem comparative with others, it makes imported labor and products more costly. This can prompt higher generally speaking costs in the homegrown market. Speculative Air pockets: Resource Cost Expansion: When costs of resources like land, stocks, or digital currencies rise quickly because of theoretical ventures, it can prompt expanded riches and spending. This can add to expansion in different areas.
- Administrative Changes:
- Tax assessment or Duties: Changes in charge strategies or the presentation of levies can straightforwardly affect the costs of labor and products. This can prompt expansion in the event that makers give the extra expenses for buyers. Regular Occasions: Crop Disappointments or Catastrophic events: These occasions can prompt discounted farming result, bringing about marked down supply and higher food costs. Market Power and Imposing business models: Firms with critical market power can set costs higher than would happen in a serious market. This can prompt inflationary tensions, particularly on the off chance that purchasers have restricted other options.
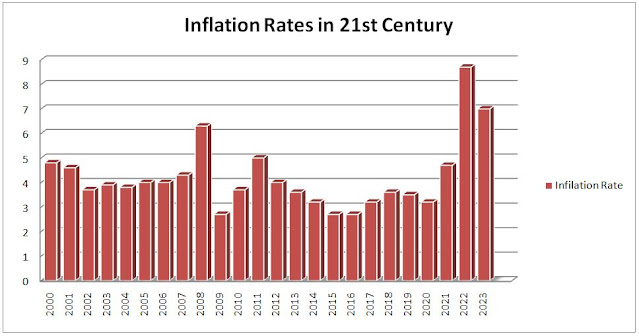
Inflation Rate in 21st Century :
The Beginning of the Thousand years (2000-2005)
As the world invited the new thousand years, the worldwide economy confronted a time of moderately consistent expansion. From 2000 to 2003, the expansion rate drifted around 4.8%, showing a moderate however steady ascent in costs. This period was described by financial dependability, with numerous countries appreciating consistent development and innovative progressions. Nonetheless, in 2004, there was a slight plunge to 4.6%, flagging an impermanent help from rising costs.10 years of Financial Changes (2006-2015)
The mid-2000s saw a change in inflationary patterns. From 2006 to 2010, expansion rates step by step declined, showing a remarkable drop to 3.7% in 2009. This period was interspersed by the worldwide monetary emergency of 2008, a seismic occasion that had expansive results on the world economy. The resulting years were set apart by careful recuperation endeavors, as legislatures and monetary organizations attempted to balance out business sectors and reestablish certainty. Before very long, from 2011 to 2015, expansion rates remained generally steady, wavering somewhere in the range of 3.6% and 4.3%. The worldwide economy was portrayed by a fragile difficult exercise among development and regulation, with different districts encountering various paces of recuperation. Factors, for example, changes in buyer interest, variances in product costs, and changes in money related strategy assumed critical parts in moulding these inflationary patterns.Another Monetary Scene (2016-2023)
The last option some portion of the 21st century's subsequent ten years saw a more different scope of inflationary examples. From 2016 to 2020, expansion rates commonly stayed inside the scope of 2.7% to 3.9%. These years were set apart by a mix of consistent monetary development and careful idealism, tempered by progressing international vulnerabilities and mechanical headways. In any case, 2020 ended up being an essential year, with the beginning of the Coronavirus pandemic. This uncommon worldwide occasion had significant monetary repercussions, prompting a flood in expansion to 8.7% - the most noteworthy in more than twenty years. The pandemic disturbed supply chains, adjusted purchaser conduct, and provoked broad government mediations to settle economies. As the world wrestled with the difficulties of the pandemic, the next years saw purposeful endeavors to reestablish monetary balance. Expansion rates in 2021 and 2022 stayed raised at 7% and 5% separately, mirroring the intricacies of recuperation. Legislatures and national banks carried out a scope of strategies, including upgrade bundles and changes in accordance with loan fees, to moderate the effects of the pandemic on the two organizations and people. In 2023, there was a slight decline in expansion to 4.7%, flagging a possible re-visitation of a more settled monetary scene. Nonetheless, it's critical to take note of that the outcome of such a significant occasion as the pandemic can keep on resonating through economies into the indefinite future.Expansion, the supported expansion in the general value level of labour and products after some time, is a basic monetary peculiarity that straightforwardly influences people, organisations, and states. From 2016 to 2023, the world saw a different cluster of inflationary patterns, impacted by a juncture of financial, international, and innovative variables. Understanding the basic reasons for these inflationary examples during this period is critical for settling on informed monetary choices and concocting viable approaches.
1. Production network Interruptions (2019-2023)
One of the most noticeable drivers of expansion in the last 50% of this period was the far reaching disturbance of worldwide stockpile chains. The Coronavirus pandemic, which arose in late 2019, set off an outpouring of disturbances underway, transportation, and dispersion. Lock downs, plant terminations, and limitations on development essentially hampered the creation and conveyance of labor and products. Therefore, shortage of specific items and expanded creation costs added to rising costs.2. Boost Bundles and Money related Approach (2020-2023)
Because of the financial strife fashioned by the pandemic, states all over the planet carried out enormous scope improvement bundles. While these actions were fundamental in settling economies and forestalling broad monetary breakdown, they likewise brought a flood of cash into course. With more cash accessible, interest for labor and products expanded, which, thus, pushed costs upwards. Besides, national banks answered the emergency by keeping up with low financing costs, which further supported buyer spending and speculation, sustaining the inflationary tensions.3. Item Value Vacillations (2016-2023)
The costs of unrefined components and products experienced huge instability during this period. Factors, for example, international pressures, environment related occasions, and changes in worldwide interest all assumed parts in driving these vacillations. For example, the fluctuating costs of oil, a basic contribution to numerous businesses, significantly affected transportation, assembling, and energy costs. These changes underway expenses were in the long run given to purchasers as greater costs for labour and products.4. Work Market Elements (2016-2023)
The elements of the work market likewise assumed a part in expansion patterns. In specific areas, there was expanded contest for gifted work, which prompted wage increments. While higher wages can animate customer spending, they can likewise add to expansion on the off chance that not adjusted by comparing expansions in efficiency. At times, organizations gave higher work expenses for customers through greater costs for their items and administrations.5. Financial Development and Quantitative Facilitating (2016-2023)
National banks, with an end goal to invigorate financial development and check deflationary tensions, participated in different types of money related extension and quantitative facilitating. These arrangements include the acquisition of government protections and bonds to infuse liquidity into the monetary framework. While viable in animating getting and venture, they likewise increment the cash supply, which can add to inflationary tensions.6. International Occasions and Exchange Questions (2016-2023)
International pressures and exchange questions between significant economies straightforwardly affected expansion. Taxes and exchange limitations forced by different legislatures upset the progression of products and inflated costs for organizations associated with global exchange. These inflated expenses were frequently given to buyers, adding to expansion. All in all, the reasons for expansion in the years 2016-2023 were diverse and moulded by a complicated exchange of monetary, international, and mechanical elements. The Coronavirus pandemic and its resulting disturbances, combined with extensive financial and money related strategies, were critical drivers. Furthermore, changes in product costs, work market elements, and international occasions generally assumed critical parts. Understanding these causes gives significant experiences to policymakers and people the same in exploring the monetary scene of the 21st hundred years.Suggestions To Reduce Inflation :
Suggestions To Reduce Inflation :
Money related Approach:
Fixing Financial Stock: National banks can execute approaches to decrease the cash supply development rate. This can be accomplished by expanding loan fees, which makes getting more costly and decreases spending. Open Market Tasks: National banks can offer government protections to business banks, which lessens how much cash available for use, checking inflationary tensions. Save Necessities: By expanding the level of stores that banks should hold as stores, national banks can restrict their loaning limit, diminishing the cash supply. Forward Direction: Clear correspondence about future money related approach goals can impact market assumptions and assist with overseeing inflationary tensions.
- Monetary Approach:
- Diminishing Government Spending: Severity measures, like cutting pointless costs and smoothing out government activities, can decrease the general interest in the economy, checking expansion. Increasing government rates: Expanding duties can lessen extra cash, hosing shopper spending and dialling back expansion. Adjusted Financial plans: States can hold back nothing, where consumption match incomes. This forestalls unreasonable cash supply development. Public Speculation Proficiency: Assuming the public authority keeps on putting resources into foundation and improvement projects, it ought to guarantee effectiveness and efficiency to forestall inflationary tensions.
- Supply-Side Arrangements:
- Further developing Efficiency: Empowering mechanical headway, putting resources into instruction, and giving preparation projects can upgrade efficiency, decreasing creation costs and inflationary tensions. Tending to Store network Issues: Strategies that emphasis on limiting disturbances in supply chains can forestall cost-move expansion by guaranteeing a consistent progression of labour and products. Market Rivalry: Empowering contest in business sectors keeps syndication from setting costs higher than serious levels.
- Pay and Value Controls:
- Transitory Measures: In specific conditions, state run administrations might consider executing impermanent compensation and value controls to oversee expansion straightforwardly. Nonetheless, these actions are many times seen as momentary arrangements and may have potentially negative side-effects. Expansion Focusing on: Clear Targets and Correspondence: Laying out a particular expansion target and imparting this objective to general society can assist with mooring expansion assumptions, directing financial way of behaving. Swapping scale Arrangements: Keeping up with Stable Trade Rates: Guaranteeing a steady swapping scale can assist with forestalling imported expansion, as changes in money esteem influence the costs of imported products. Administrative Changes: Decreasing Obstructions to Section: Empowering rivalry by lessening administrative boundaries for new organisations can increment market proficiency and forestall cost climbs. Further developing Business Climate: Smoothing out administrative cycles, guaranteeing property privileges, and limiting defilement can support speculation and rivalry, which can add to stable costs.
- Public Correspondence and Training:
- Expansion Mindfulness Missions: Instructing people in general about expansion, its causes, and its effects can prompt more educated monetary choices and ways of behaving. Worldwide Collaboration:Planning Strategies: Cooperation between countries can assist with settling the worldwide economy, keeping outer shocks from causing boundless expansion.It's essential to take note of that the viability of these actions can change contingent upon explicit monetary circumstances, and executing them ought to be painstakingly custom fitted to the extraordinary conditions of every country. Moreover, a reasonable methodology that thinks about both present moment and long haul objectives is essential for supported progress in decreasing expansion rates.
It's critical to take note of that the viability of these actions can fluctuate contingent upon explicit monetary circumstances, and carrying out them ought to be painstakingly customised to the special conditions of every country. Furthermore, a decent methodology that thinks about both present moment and long haul objectives is significant for supported progress in lessening expansion rates.




Comments
Post a Comment